
If a large number of worms are present in the body, the host may experience vomiting, shortness of breath, swelling in the abdomen or blockages in the intestines.Ī dish of Ascaris lumbricoides worms. Around 85% of people who are infected with Ascaris lumbricoides do not show any symptoms, particularly if the number of worms in the body is low. Ascaris lumbricoides is most prevalent in tropical and sub-tropical regions of the world, particularly those areas with poor sanitation. They travel to the stomach before entering the intestines where they live. They are then coughed up out of the lungs into the mouth and consequently swallowed. The eggs hatch in the intestines and migrate to the lungs. Their eggs are deposited into soil in faeces and are transmitted to humans via contaminated food or drink. Ascaris lumbricoides is the giant roundworm that infects humans and can grow up to 35 centimetres long. Giant roundworms are very long (often over 30 centimetres in length) and vary in diameter from two to six millimetres. There are thousands of different species of roundworm, several of which infect humans. The medication often works by interfering with the worm’s movement or metabolism. Roundworm infections can be successfully treated with medication, either a course of tablets or a powder that is dissolved in water for young infants. Gut worms are the most prevalent and can be diagnosed by looking under a microscope for worms or eggs in samples of faeces. Disease can be caused by the worm living in the gut, blood, lymph or tissues. Roundworm infections usually do not cause noticeable symptoms unless the worms are present in very large numbers.  Infections of roundworm happen more often in warm, tropical climates in poor, rural communities. Roundworms range in length from less than a millimetre to a metre. an insect, such as a mosquito, carrying the worm bites a host.
Infections of roundworm happen more often in warm, tropical climates in poor, rural communities. Roundworms range in length from less than a millimetre to a metre. an insect, such as a mosquito, carrying the worm bites a host. Number of hookworms in humans skin#
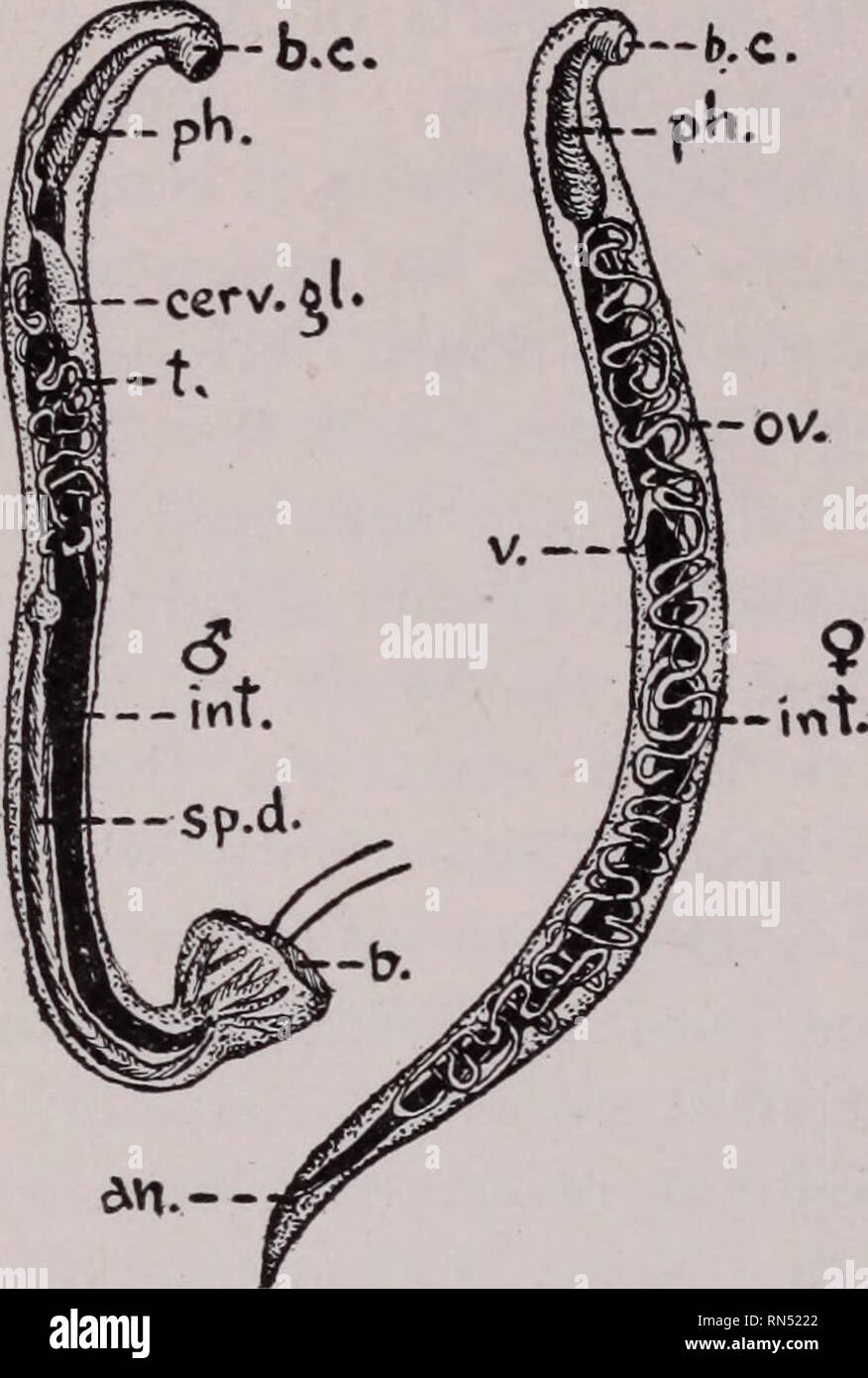
the worm directly penetrates the host's skin.the host eats food or drinks water containing the worms.The worms can get into a host's body when:.Roundworms, or nematodes, are slender worms that can live, feed and reproduce in the human intestine.They are grouped according to their general shape and the part of the host they tend to affect and live in during infection. Knowing how they function and cause disease is expected to lead to new, more effective ways of treating these infections.īelow is an introduction to some of the best characterised helminth worms.It is hoped that knowing more about the genomes of other helminths could provide useful insights into their biology.elegans is a very simple organism, sequencing its genome paved the way to a comprehensive view of its development and behaviour.

Caenorhabditis elegans, a roundworm (or nematode) with around 1,000 cells, was the first animal to have its genome sequenced.The global burden of helminth disease exceeds that of conditions such as malaria and tuberculosis.

Infection can cause physical, nutritional and cognitive impairment in young, developing children. That's almost a third of the world's population! Helminths are one of the leading causes of morbidity in the developing world with over two billion people affected. Their effects inside their host also vary, causing a wide spectrum of diseases, from mild to potentially deadly. Helminths infect a range of hosts, including humans. There are many different kinds of helminth ranging in length from less than one millimetre to over one metre. All helminths are invertebrates with long, flat or round bodies. ‘Helminth’ is a general term meaning worm.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
